Protein Guideprotein basics for beginners
How is protein used in the body?
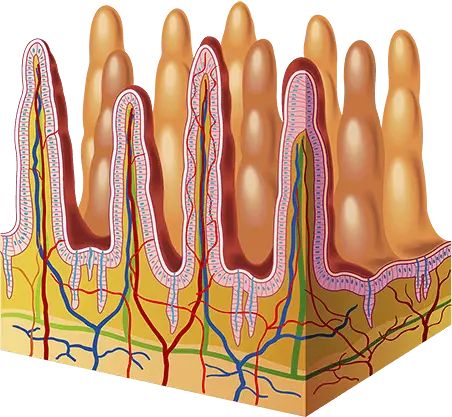
When you consume protein, it's digested in the stomach where acid and enzymes called proteases break down the peptide bonds to create smaller amino acid chains. These smaller amino acid chains then move through to your small intestine. Here, additional enzymes go to work, further breaking down these short chains into individual amino acids.
Your small intestine is made up of villi, which are finger-like structures that increase surface area and nutrient absorption. These villi are covered in special transporter cells that allow amino acids to be absorbed into your bloodstream. From your bloodstream, these amino acids are transported for use by every part of your body.
While your body can create most of the amino acids required for healthy growth, there are 9 amino acids you must absorb from consumed protein. These 9 amino acids are often referred to as the “Essential Amino Acids”, as these must be consumed for the human body to remain healthy. When selecting good protein it's important to consider a source that contains good levels of all these essential amino acids.
Your small intestine is made up of villi, which are finger-like structures that increase surface area and nutrient absorption. These villi are covered in special transporter cells that allow amino acids to be absorbed into your bloodstream. From your bloodstream, these amino acids are transported for use by every part of your body.
While your body can create most of the amino acids required for healthy growth, there are 9 amino acids you must absorb from consumed protein. These 9 amino acids are often referred to as the “Essential Amino Acids”, as these must be consumed for the human body to remain healthy. When selecting good protein it's important to consider a source that contains good levels of all these essential amino acids.
Leucine
Leucine is by far the highest percentage of amino acids found in whey protein. It's also the fourth most concentrated amino acid found in muscle tissue. This important amino acid stimulates muscle growth. Leucine is also the amino acid responsible for activating an essential compound in cells called mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin). This regulates several cellular processes for growth and also includes nutrient transport. This makes Leucine essential for not just muscle development but energy synthesis by muscle cells. Leucine is essential for endurance. Leucine also helps to regulate your levels of blood sugar by moderating insulin in the body during and after exercise.
Leucine
Complete
Protein
Protein
Foods rich in Leucine:
Cheese, soybeans, meat and fish, dairy and eggs, pumpkin, lentils, chickpeas, corn, rice, almonds, peas, oats, whey protein, and plant protein.
Isoleucine
Isoleucine helps with endurance and assists in the repair and building of muscle. It's an isolated form of leucine that helps the body produce hemoglobin. Hemoglobin carries iron in the blood and regulates blood sugar which is burned for energy in muscles. Isoleucine also mediates glucose uptake and its breakdown into energy within muscle cells.
Isoleucine
Complete
Protein
Protein
Foods rich in Isoleucine:
Soybeans, meat, and fish, dairy and eggs, cashews, almonds, oats, lentils, brown rice, legumes, and chia seeds.
Lysine
Lysine is an essential amino acid responsible for muscle repair and growth. It also plays an important role in building a healthy immune system, increasing appetite, and digestion. Lysine is also used to produce hormones, enzymes, and antibodies. Lysine also helps with the absorption of other minerals in the body including calcium. Lysine also aids in the synthesis of collagen that is needed for the creation of connective tissue and bones.
Lysine
Complete
Protein
Protein
Foods rich in Lysine:
Meat and fish, dairy and eggs, soybeans, peas, cheese, potatoes, chia seeds, parsley, avocados, almonds, cashews, and whey protein.
Methionine
Methionine is essential for the growth of new blood vessels, muscle growth, and a healthy heart. Methionine contains sulfur, which is essential for muscle and tissue health. Insufficient levels of sulfur can lead to tissue damage and difficulty healing. Methionine is essential for muscle growth and the formation of creatine, which is needed for muscle energy. Methionine also helps dissolve fat within the body and its conversion to be used for energy.
Methionine
Complete
Protein
Protein
Foods rich in Methionine:
Meat and fish, dairy and eggs, beans, brazil nuts, oats, wheat, figs, whole grain rice, beans, and onions.
Phenylalanine
Phenylalanine is turned into the amino acid tyrosine within the body, which is needed to produce proteins and neurotransmitter chemicals such as epinephrine, L-dopa, and norepinephrine. Phenylalanine can help with depression and lethargy. It is also important for pain control. It is also used to produce endorphins during exercise.
Phenylalanine
Foods rich in Phenylalanine:
Meat and fish, dairy and eggs, seaweed, pumpkin, beans, rice, peanuts, almonds, quinoa, avocado, figs, raisins, and olives.
Threonine
Threonine is used for the formation of cartilage, bones, hair, teeth, and nails. Its also important in the growth of skeletal muscles, the heart, liver, and intestine. Threonine helps produce antibodies that support the immune system. Threonine is used to create glycine and serine which are necessary to produce elastin, collagen, and muscle tissue. Threonine helps to accelerate the healing of tissue damage for faster recovery.
Threonine
Complete
Protein
Protein
Foods rich in Threonine:
Meat and fish, dairy and eggs, watercress, pumpkin, avocados, hemp seeds, soybeans, almonds, figs, raisins, and quinoa.
Tryptophan
Tryptophan is used to make serotonin and melatonin which are neurotransmitters that help lower stress and reduce depression. Tryptophan has a relaxing effect on your body and aids with healthy sleeping patterns. In adults, it helps with nitrogen balance. In infants its important for growth and particularly important for the brain to develop sleep cycles. Your liver also uses Tryptophan to make make vitamin B-3 (niacin) which helps regulate metabolism.
Tryptophan
Complete
Protein
Protein
Foods rich in Tryptophan:
Meat and fish, dairy and eggs, chocolate, chickpeas, almonds, sunflower seed, bananas, and peanuts.
Valine
Valine works alongside leucine and isoleucine to repair tissues and promote muscle growth. Valine also helps with the supply of glucose to muscles for energy synthesis. This makes it essential for endurance during physical activity. Valine also helps with the delivery of nitrogen to all the organs of your body and is especially important for liver health. Valine is also important for your central nervous system and healthy mental function.
Valine
Complete
Protein
Protein
Foods rich in Valine:
Meat and fish, dairy and eggs, beans, broccoli, spinach, chia seeds, avocado, figs, blueberries, cranberries, apples, oranges, and apricots.
Histidine
Histidine is often described as both an essential and nonessential amino acid. The body can make this amino acid in limited quantity but needs additional supply. Histidine is used to develop the myelin sheath that coats nervous cells to protect them. It is also used to create the neurotransmitter histamine. It also helps with the production of red and white blood cells which are needed for overall health and immunity.
Histidine
Complete
Protein
Protein
Foods rich in Histidine:
Meat and fish, dairy and eggs, soybeans, chia seeds, buckwheat, and potatoes.
How much protein do I need?
hello world!
The content on this site has not been written, reviewed or endorsed by a medical professional. We assume no liability for the misuse of supplements and recommend you review the label of any product, as well as consulting with your health care professional.
We are a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for us to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.
We are a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for us to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.
© 2025 ProteinPowder.com


